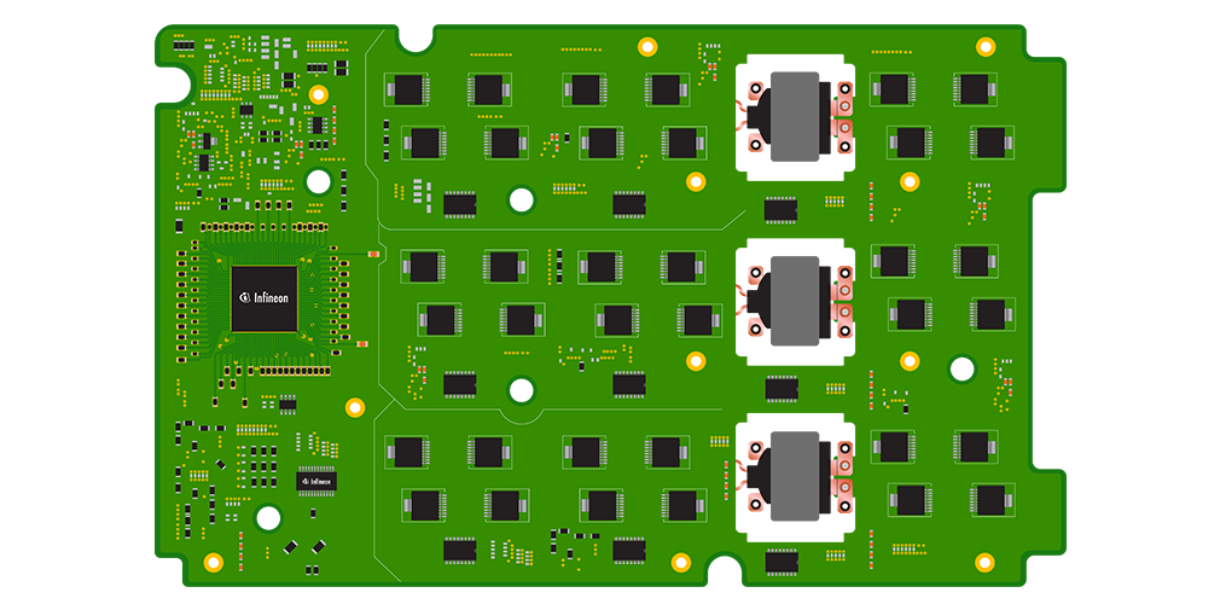
(H)EV-Bord-Batterieladegerät
Empfohlene ICs für Ihre Topologie, Referenzdesigns, Platinen und Designressourcen von Antriebsstrangsystemen für erhöhte Reichweite bei vollem Drehmoment
Das im Fahrzeug eingebaute Bord-Ladegerät (OBC) dient zum Aufladen der Hochspannungsbatterie aus dem Wechselstromnetz, wenn das Fahrzeug steht. Größere Reichweiten für Plug-in-Hybridfahrzeuge (PHEV) und batteriebetriebene E-Autos (BEV) lassen sich durch eine Erhöhung der Batteriekapazität sowie durch elektronische Komponenten mit höherer Energieeffizienz erreichen. Bei den Spannungen für die verwendeten Batterien geht der Trend zu einer Standardisierung bei etwa 450 V mit einer Tendenz zu höheren Spannungen, da damit schnellere Ladezeiten und eine leichtere Verkabelung innerhalb des Fahrzeugs möglich sind. Für Bord-Ladegeräte werden häufig diskrete Hochspannungskomponenten verwendet, da modulbasierte Lösungen aufgrund des Kostendrucks zunehmend weichen müssen. Der Trend hin zu schnellen Ladevorgängen hat auch Auswirkungen auf die für OBC-Topologien geforderte Leistungsbereiche. Daher müssen neue Designs für Leistungen von 11 kW oder sogar bis zu 22 kW ausgelegt werden. Diese Entwicklung ist in Kombination mit dem Bedarf an hohen Wirkungsgraden und Leistungsdichten bei niedrigen Systemkosten eine starke Triebfeder für den Einsatz dreiphasiger Lösungen. Bei heute üblichen Anwendungen ist die Richtung des Stromflusses unidirektional, geht also vom Stromnetz zur Batterie, aber es gibt auch Anwendungen wie „Battery-to-load“ oder „Battery-to-grid“, bei denen der Stromfluss in beide Richtungen möglich ist.
Im Blockdiagramm unten finden Sie eine Auswahl empfohlener Produkte:
Systemdiagramm für (H)EV-Bord-Batterieladegeräte
Systemvorteile
- Geeignet für Plug-in-Hybridfahrzeuge und reine Elektrofahrzeuge
- Integrierte Leistungsfaktorkorrektur (PFC-Schaltung)
- Galvanische Isolierung
- Große Auswahl von unterstützten Eingangs- und Ausgangsspannungen
- Anpassbare Stromgrenzwerte
- Nutzung der Automobil-Standardkommunikation (CAN-Bus)
- Modulares Konzept für 1- bis 3-phasiges Laden mit Wechselstrom
Beispiel für ein 3-phasiges Bord-Ladegerät:
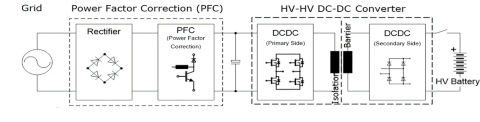
PFC-Stufe:
- Korrekturfaktor > 0,9
- Regelung der Zwischenkreisspannung
- EMV-Eingangsfilter
- Isolierung gegen Erde
—> wird typischerweise über eine Standard-Aufwärtswandlertopologie oder Totempfahl-Topologie realisiert
HV-HV-Gleichstromwandler:
- Regelung der OBC-Ausgangsspannung
- Einstellung des Ladestroms
- Galvanische Isolierung
- EMV-Ausgangsfilter
—> wird typischerweise über eine LLC-Topologie oder eine ZVS-Topologie mit Phasenverschiebung realisiert

Vorteile:
- Für alle erforderlichen Leistungsklassen von 2,3 kW bis 22 kW geeignet
- Kostenoptimierte Lösung (begrenzte Anzahl von Leistungshalbleitern)
- Einfache Implementierung
Nachteile:
- Geringerer Wirkungsgrad (Verluste im Gleichrichter)
- Keine bidirektionale Implementierung möglich
Empfohlene Produkte für
- Schalter: TRENCHSTOP™ 5-Automotive-IGBTs oder CoolMOS™-Automotive-MOSFETs
- Dioden: CoolSiC™-Automotive-Schottky-Dioden
- Gate-Treiber-ICs: Pegelumsetzer-ICs für den Automotive-Bereich
- Mikrocontroller: AURIX™-Automotive-Mikrocontroller TC2xxx oder TC3xx
- Kommunikation und System-Power-Management: OPTIREG™-LDO in Kombination mit CAN-Transceivern oder integrierten Lösungen wie SBC (System Basis Chips)

Vorteile:
- Für alle erforderlichen Leistungsklassen von 2,3 kW bis 22 kW geeignet
- Höherer Wirkungsgrad bei aktiver Gleichrichtung
- Problemlos auf bidirektionale Ladevorgänge aufrüstbar
Nachteile:
- Höhere Kosten (mehr Komponenten)
- Komplexere Implementierung
- Weniger Erfahrung auf Kundenseite hinsichtlich der Ansteuerung von schnell schaltenden IGBTs
Empfohlene Produkte für
- Schalter: TRENCHSTOP™ 5-IGBTs für den Automotive-Bereich
- Gleichrichtung: CoolMOS™-Automotive-MOSFETs oder CoolSiC™-Automotive-Siliziumcarbid-MOSFETs
- Gate-Treiber-ICs: Pegelumsetzer-ICs für den Automotive-Bereich
- Mikrocontroller: AURIX™-Automotive-Mikrocontroller TC2xxx oder TC3xx
- Kommunikation und System-Power-Management: OPTIREG™-LDO in Kombination mit CAN-Transceivern oder integrierten Lösungen wie SBC (System Basis Chips)

Vorteile:
- Für alle erforderlichen Leistungsklassen von 2,3 kW bis 22 kW geeignet
- Weit verbreitet in Industrie- und Consumer-Anwendungen
- Keine Drosselspule zum Herausfiltern von Stromwelligkeit am Ausgang erforderlich
- Einfache Aufrüstung auf bidirektionalen Betrieb
Nachteile:
- Komplexer Regelalgorithmus
- Exakte Berücksichtigung der Resonanzfrequenz durch die Regelung erforderlich
- Ein Ausfall der Regelung führt zu einer Beschädigung des OBC
- Konstanter Eingangsstrom erforderlich
Empfohlene Produkte für
- Schalter: CoolMOS™-Automotive-MOSFETs oder CoolSiC™-Automotive-Siliziumcarbid-MOSFETs
- Gleichrichtung: CoolSiC™-Automotive-Schottky-Dioden
- Gate-Treiber-ICs: Pegelumsetzer-ICs für den Automotive-Bereich
- Mikrocontroller: AURIX™-Automotive-Mikrocontroller TC2xxx oder TC3xx
- Kommunikation und System-Power-Management: OPTIREG™-LDO in Kombination mit CAN-Transceivern oder integrierten Lösungen wie SBC (System Basis Chips)

Vorteile:
- Für alle erforderlichen Leistungsklassen von 2,3 kW bis 22 kW geeignet
- Weit verbreitet in Industrie- und Consumer-Anwendungen
- Keine Drosselspule zum Herausfiltern von Stromwelligkeit am Ausgang erforderlich
- Einfache Aufrüstung auf bidirektionalen Betrieb
Nachteile:
- Komplexer Regelalgorithmus
- Exakte Berücksichtigung der Resonanzfrequenz durch die Regelung erforderlich
- Ein Ausfall der Regelung führt zu einer Beschädigung des OBC
- Konstanter Eingangsstrom erforderlich
Empfohlene Produkte für
- Schalter: CoolMOS™-Automotive-MOSFETs oder CoolSiC™-Automotive-Siliziumcarbid-MOSFETs
- Gleichrichtung: CoolSiC™-Automotive-Schottky-Dioden
- Gate-Treiber-ICs: Pegelumsetzer-ICs für den Automotive-Bereich
- Mikrocontroller: AURIX™-Automotive-Mikrocontroller TC2xxx oder TC3xx
- Kommunikation und System-Power-Management: OPTIREG™-LDO in Kombination mit CAN-Transceivern oder integrierten Lösungen wie SBC (System Basis Chips)
Online Courses
This training covers the harmonized frame of standards from international bodies like ISO, IEC, SAE and UL dedicated to the Wireless Power Transfer system technologies.
This training covers the most relevant standards for high power charger design, grouped into 4 major areas:
• charging topology
• communication
• accessories
• safety and security
Do you want to know the various topologies you can find in this power conversion stage and their top-level working principle? Get to know the basic concepts of passive and two-level active rectification methods.

Understand why to use WBG switches for bi-directional converters, the topologies used and how they function.

Training topics:
- Get to know how AURIXTM is able to answer the needs of the electric vehicle market
- Recognize and explore how AURIX™ TC3xx addresses key electric vehicle challenges, and understand the main features of the AURIX™ TC3xx microcontroller

In this training you will:
- Get to know Infineon’s IPOSIM tool, specifically for an automotive electric vehicle inverter
- Discover the steps involved in simulating different parameters and comparing the results of different Infineon products to see which is the best fit for your application
- The training covers detailed information about Infineon's 3rd generation automotive EiceDRIVER™ 1EDI305xAS
- Participants will learn how these products help to reduce switching losses and improve thermal efficiency, resulting in longer range for hybrid and electric vehicles
This training covers Infineon’s portfolio of power semiconductors, ranging from D2PAK packages to 62-millimeter modules.
All products are based on the latest micro-pattern trench technology.

In this training you will:
- Be familiar with silicon carbide MOSFET structures and their characteristics
- Get to know Infineon's CoolSiC™ MOSFET, its features, its improvements over a typical trench MOS and how it performs against its competitors

In this video, you will:
- Be familiar with top-side cooling, its uses and benefits
- Learn how you can get the most out of your TOLT package

In this training you will:
- Understand the benefits that SiC technology has over Si technology in products and systems
- Recognize the benefits of SiC in automotive applications

Training topics:
- Get to know how AURIXTM is able to answer the needs of the electric vehicle market
- Recognize and explore how AURIX™ TC3xx addresses key electric vehicle challenges, and understand the main features of the AURIX™ TC3xx microcontroller

In this video you will:
- See how charging works inside a car
- Be familiar with the concept of an onboard charger (OBC) and the different charging categories
- Recognize the requirements for onboard charging and identify different power topologies

In this video you will:
- Understand what Battery Electric Vehicle charging is
- Recognize the three different charging categories available
- Know how these categories can be implemented

In this video, you will:
- Understand how Infineon’s power semiconductor module portfolio is a solution for the main challenges of the electric vehicle industry
- Know Infineon’s general value drivers as well as recent success stories on the electromobility market

In this training you will:
- Be familiar with silicon carbide MOSFET structures and their characteristics
- Get to know Infineon's CoolSiC™ MOSFET, its features, its improvements over a typical trench MOS and how it performs against its competitors

Get to know our 2020 joined CoolMOS™ SJ MOSFET family member: the CFD7A!

Training topics:
- Get to know why systems require frequent updates, how this is done and how automotive systems try to ensure their security when they are updated
- Learn how AURIX™ families of microcontrollers support over-the-air software updates