Automotive power distribution
Optimize your E/E architecture with a decentralized and electrified automotive power distribution system (PDS)
Please choose a subcategory
Infineon's automotive power distribution solutions
Discover the power of seamless energy control with Infineon's automotive power distribution solutions. Rigorously tested to meet the highest standards of performance and reliability across diverse applications, Infineon offers the broadest chipset portfolio for semiconductor-based power distribution units (PDUs). Our PROFET™ smart power switches, MOSFETS and corresponding gate drivers are best-in-class in terms of current scalability and adaptability. While the AURIX™ family enables integration of power distribution functions with high-end computing performance applications, such as zone controllers, the TRAVEO™ microcontrollers serve as a complementary low-end alternative for price-performance optimized power distribution. Complementing this lineup are Infineon's XENSIV™ sensors, OPTIREG™ power supply solutions and communication transceivers, creating a highly interoperable chipset with pin-to-pin compatibility where it matters. This ensures easy adaptation and migration for evolving power distribution unit requirements. Infineon’s commitment to quality and innovation simplifies design challenges and accelerates your time-to-market.
Streamline your automotive power distribution unit designs
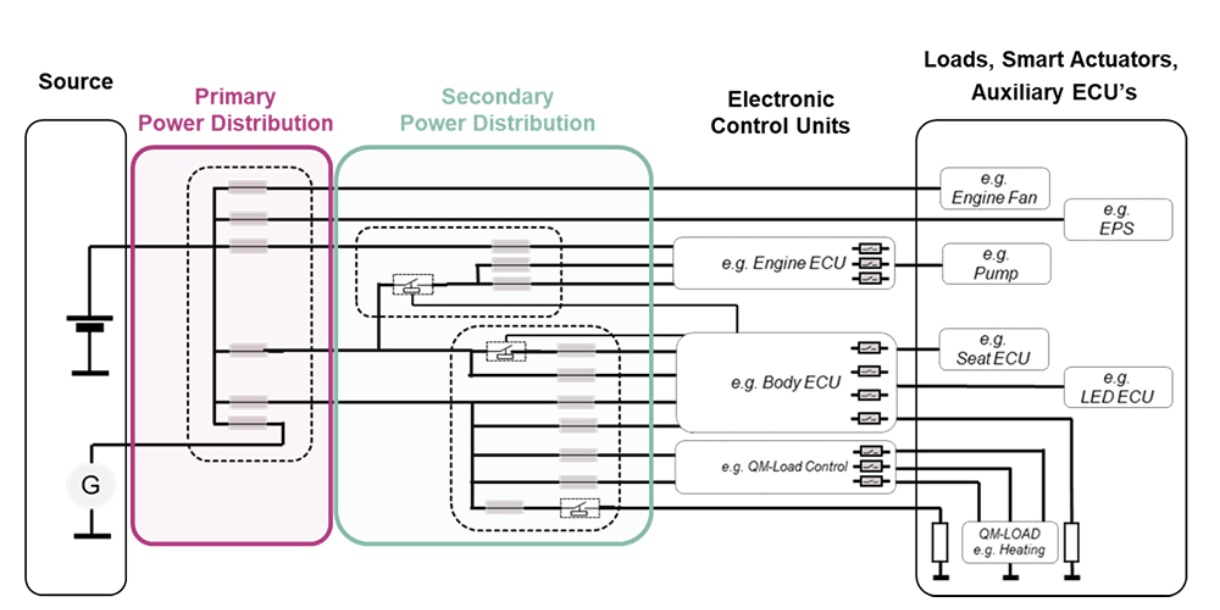
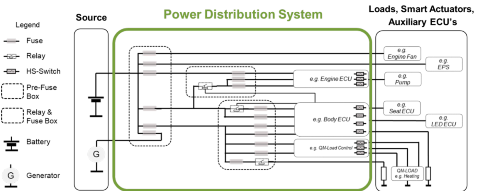
Power distribution is a key function of the E/E architecture. Automotive power distribution systems control the transport of low-voltage electric energy via the wire harness. The PDS design choices are particularly essential for power distribution in electric vehicles, where efficient energy management is crucial. The PDS consists of two main elements - the primary power distribution unit and the secondary power distribution unit. The primary PDU is connected to the energy source (i.e. a battery or a DC-DC) and often referred to as the pre-fuse box. Energy then flows to one or several secondary power distribution units, which eventually distribute the energy to all low-voltage loads of the vehicle. As a consequence of an increasing number of comfort and AD(AS) functions, the number of these loads has sharply increased in recent years. Subsequently, the automotive power distribution system has become increasingly complex. Infineon supports its customers in dealing with this complexity through its bottom-up product-to-system expertise and its broad product portfolio, optimized for scalable power distribution systems.

The three generations of power distribution systems
Upon closer observation, three generations of automotive low-voltage power distribution systems exist. While all PDS implementations will eventually converge towards generation 3, the generations currently co-exist in the market.
In generation 1, both the primary and the secondary power distribution unit, are solely built on (electro-)mechanical solutions. The amount of secondary power distribution units is little and fuses and relays control the energy flow.
Generation 2 strives for optimization of the power distribution wire harness. By placing an increased number of secondary power distribution units closer to the loads, the total length of wires is reduced. The partial replacement of fuses and relays with semiconductors, enables a higher degree of flexibility, as well as diagnosability.
Finally, generation 3 is directly linked to the introduction of zone architectures. It features the integration of the secondary power distribution unit in the zone control unit. Subsequently, optimization is not limited to the power distribution wire harness, but now also includes the in-vehicle network (IVN). At this stage, the secondary power distribution fully builds on semiconductors.
Easily adoptable ISO-26262 PDS solutions
Infineon's AURIX™ microcontrollers are best-in-class for ASIL-D functional safety designs and are complemented by the TRAVEO™ family for ASIL-B needs (partly with ASIL-D island). Corresponding OPTIREG™ power supply solutions come with easily-implementable safety manuals, enabling not only a safe design, but also a quick realization of Functional Safety goals. The PROFET™ smart power switches are ISO-ready and partly ISO-compliant with plenty of safety documentation available, allowing the overall easiest functional safety design in the market.
48 V zone architecture readiness
The growing adoption of Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) entails the electrification of mechanically-driven legacy loads, as well as an introduction of new loads. The logical consequence of this change is an increased demand for electric low-voltage power. Although not yet widely adopted, introducing an additional 48V layer to the PDS, may hold several benefits for the overall vehicle E/E architecture of BEVs. Among others, it allows to lift the intrinsic maximum power limitations of a 12V E/E architecture, and thus represents an important cornerstone for future Battery Electric Vehicles.
Infineon actively drives international standardization efforts for 48 V power distribution systems and ensures that customer solutions are in line with current and future standardization initiatives. Infineon's broad Gate Driver and MOSFET portfolio and the growing PROFET™ smart power switches portfolio enable the transition to 48 V power distribution systems with pin-to-pin compatibility where it matters.
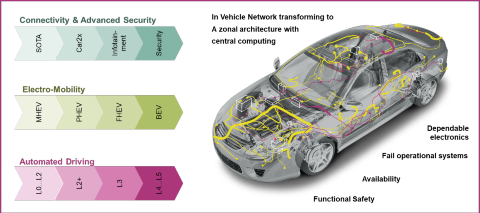
Design challenges & Infineon support
When designing modern power distribution systems, customers face a variety of challenges. They need to harmonize the automotive power distribution system and the In-Vehicle Network, with the integration of both converging to a zone architecture incl. central computing. Simultaneously, they need to introduce fail-operational concepts for a dependable power distribution through the use of semiconductor-based safety elements in the primary and secondary power distribution units. Finally, they have to optimize the overall system as such, that wire harness complexity is reduced, the increasing power demand of BEVs is satisfied and platform re-use becomes possible.
Infineon provides a series of self-support collaterals, such as a configurable block diagram to aid the selection of fitting products, whitepapers, application notes, evaluation kits and datasheets. Additionally, Infineon benefits from its position as market leader for automotive and has - over the years - built a strong bottom-up product-to-system expertise. Please contact your Infineon contact if you would like to engage further.
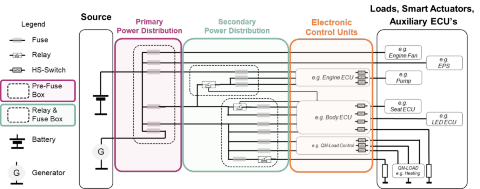
The automotive power distribution system is built on three main elements - the primary power distribution, the secondary power distribution and the electronic control units (ECUs).
The primary power distribution is close to the source, often called the pre-fuse box. The secondary power distribution as of today, is the classical relay & fuse box which can be one central box or several distributed boxes.
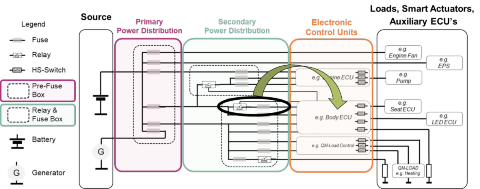
Already a decade ago, engineers started to remove relays and fuses from the secondary power distribution. The most common approach has been to move reliability-critical functions to an electronic control unit (ECU) such as the automotive body control module (BCM) where the clamp 30 (key-off) release and clamp 15 (key-on) functions are located. Replacing relays and fuses with semiconductors in this way increases the power distribution system reliability thanks to additional diagnostics and enhanced protection features.

- Smart power switches and controllers not only are they key partners for the realization of automated driving but they are also one of the founding blocks of current automotive megatrends.
- They are essential when it comes to supplying and distributing power, as well as protecting devices from excessively high current or temperature.

- Infineon’s Dual Gate MOSFET (IAUTN08S5N012L) is an 80 V product with an RDS of 1.15 milliohms, making it an ideal choice for use in disconnect switches
- Learn more about this product and its use in power distribution applications in this training

- Recognize the portfolios of PROFET™ +2 12V and Power PROFET™ and identify the advantages of each of these product families
- Distinguish the differentiating features of the newly released devices of the PROFET™ +2 12V and Power PROFET™ + 12V families

In this training, you will:
- Indicate what an electrical power distribution center is and describe what solutions Infineon offers for
- Explain why relays and fuses are being replaced with semiconductors and identify the devices that Infineon provides for replacing

Description:
- Explain how the major automotive trends are shaping the evolution of electrical and electronic or E/E architectures in cars
- Identify the trending E/E architecture concepts and their impact on networking technologies and recognize the solutions that Infineon provides to support current and future E/E architectures

In this training, you will:
- Understand what a body control module is and what solutions Infineon offers for standard and high-end body control modules
- Discover why relays and fuses are being replaced with smart switches and identify Infineon's alternative devices